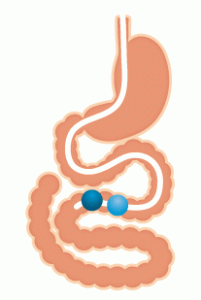
 The double-balloon enteroscopy is a procedure which is primarily used to examine sections of the small intestine. The endoscope can be inserted from the mouth and sent downwards to view the upper gut, or in the case of a retrograde enteroscope procedure, it can be sent upwards from the anus and through the colon and into the ileum.
The double-balloon enteroscopy is a procedure which is primarily used to examine sections of the small intestine. The endoscope can be inserted from the mouth and sent downwards to view the upper gut, or in the case of a retrograde enteroscope procedure, it can be sent upwards from the anus and through the colon and into the ileum.
This procedure is an invasive technique and is normally performed under general anesthetic. It can be employed to look for the presence of inflammation or Chron’s disease, to examine the condition of the surface of the small intestine, to look for cancerous growths or polyps that may be obstructing the gut, or to look for other structural abnormalities which might impede the normal flow of food.
The endoscope provides images from inside the gut that are viewed by the gastroenterologist. The procedure gets its name from the presence of two balloons on the scope which can be alternately inflated and moved in order to pull the scope along the length of the gut. In addition, tools are available to do various kinds of local surgery, for example, removing polyps, taking tissue samples, or stretching out the gut if it contains a region which is unusually narrow.
Including preparation, the procedure may take a few hours. It is necessary to be connected to an IV and hooked up to a set of machines to monitor the patient’s health during the procedure. The patient also needs to avoid eating beforehand because of the use of anesthetic.
The procedure is more invasive than a colonoscopy or upper endoscopy, and therefore carries more health risks, such as bleeding or damage to the intestine.
